ANN: Table of Contents
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
Overview
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by biological neural networks in human brains. They are designed to process complex data and perform tasks like classification, prediction, and pattern recognition.
Architecture
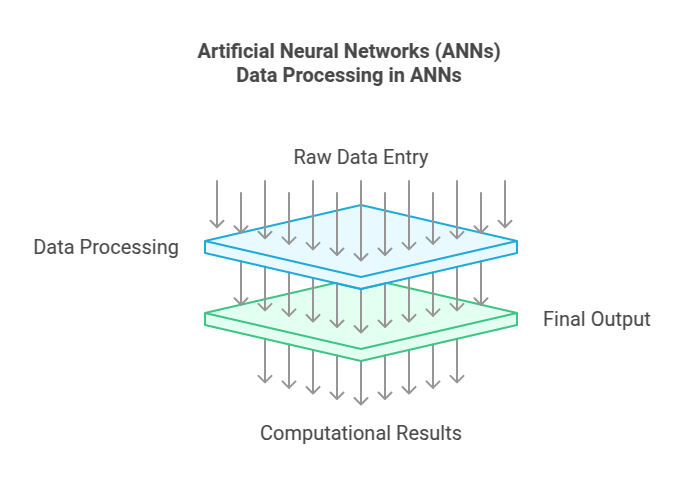
Layers:
- Input Layer: Initial point of data entry
- Hidden Layers: Process and analyze data
- Output Layer: Provides final computational results
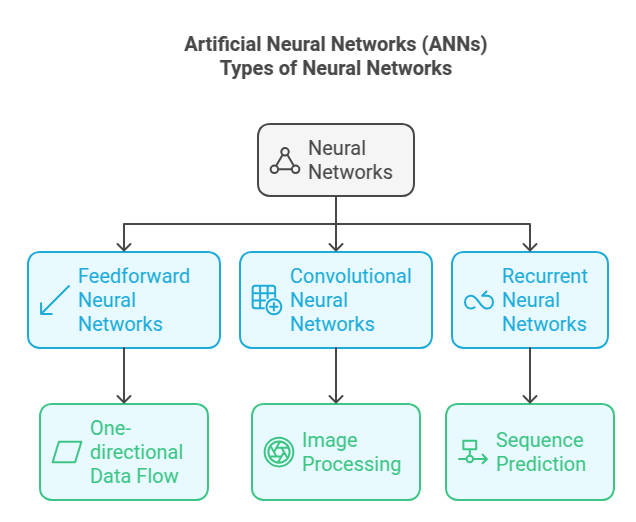
Types of Neural Networks
Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs)
- Data moves in one direction
- No cycles or loops
- Straightforward processing
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- Specialized for processing grid data (images)
- Uses convolutional layers
- Effective for image recognition
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
- Designed for sequence prediction
- Maintains context across inputs
- Useful for time-series and language processing
Training Methods
Learning Approaches:
- Supervised Learning: Uses labeled training data
- Unsupervised Learning: Discovers patterns in unlabeled data
- Reinforcement Learning: Learns through environmental interaction
Training Process:
- Forward Propagation
- Loss Function Calculation
- Backward Propagation (Backpropagation)
ANNs Mathematics
Applications
Key Areas:
- Natural Language Processing
- Healthcare
- eCommerce
- Computer Vision
Challenges
Limitations:
- Overfitting
- Lack of Interpretability
- High Training Data Requirements
- Computational Intensity
Ethical Considerations:
- Bias in decision-making
- Accountability
- Transparency in automated systems