Generative AI
Generative AI Models
Generative AI models are machine learning models that can generate new data from existing data.
Generative AI models are used in many applications, such as image generation, text generation, speech synthesis, and music generation.
Table with key technologies and models that play crucial roles in Generative AI:
| Technology | Year Released | Description | Key Differences | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | 2020 | Combines information retrieval with text generation. | Focuses on enhancing generation with retrieved data. | Chatbots, question answering systems |
| Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) | 2014 | Consists of a generator and a discriminator competing against each other. | Uses adversarial training for realistic data generation. | Image and video generation |
| Large Language Models (LLMs) | 2018 | Deep learning models trained on vast amounts of text data. | Specializes in understanding and generating human-like text. | Text generation, summarization, translation |
| GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) | 2018 | A specific type of LLM developed by OpenAI using transformer architecture. | Pre-trained on large datasets for coherent text generation. | Conversational agents, content creation |
| Autoencoders | 1987 | Neural networks for learning efficient data representations. | Composed of an encoder and decoder for data compression. | Denoising, anomaly detection |
| Transformers | 2017 | Neural network architecture using self-attention mechanisms. | Designed for processing sequential data effectively. | Natural language processing, image analysis |
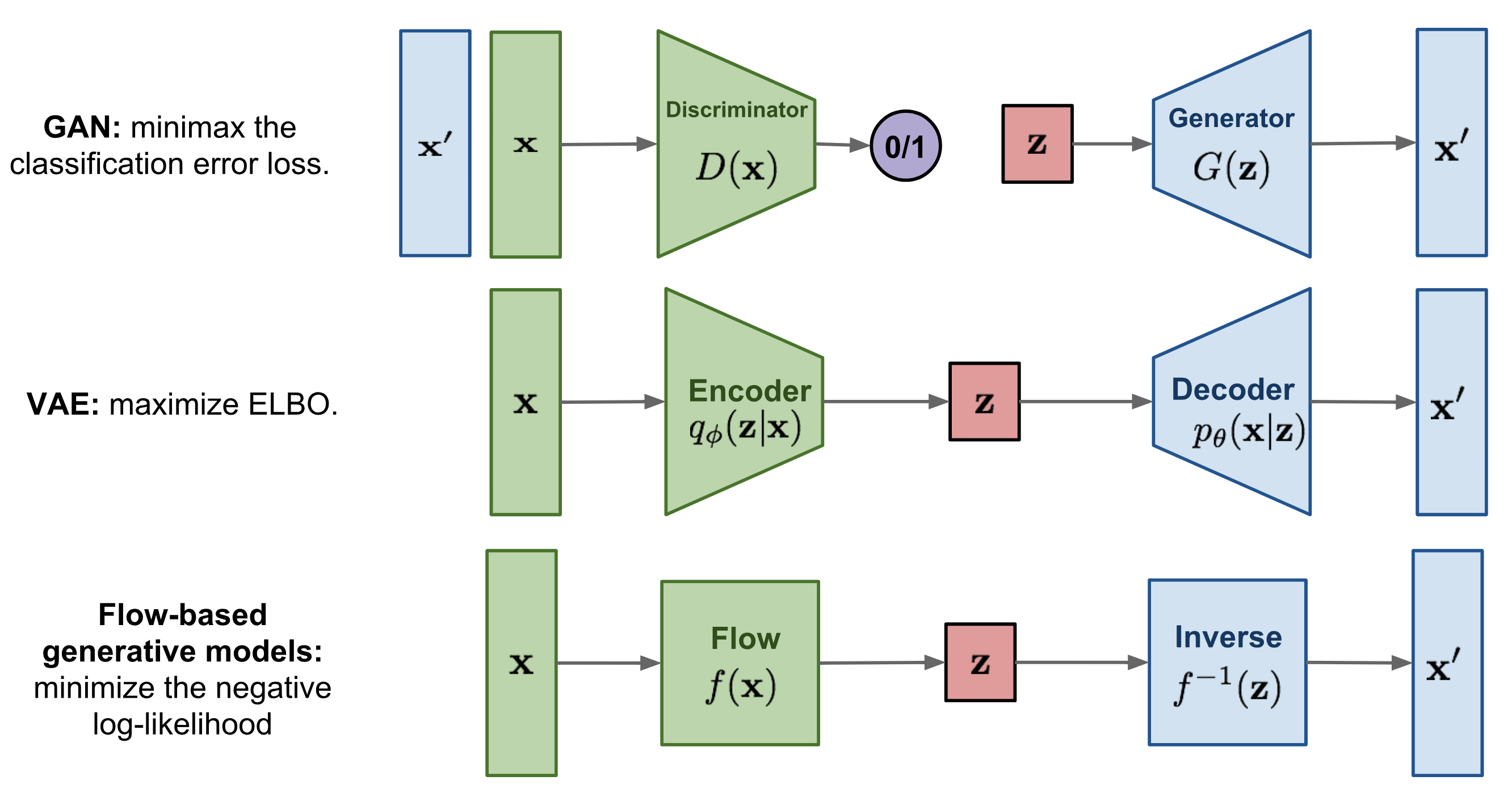
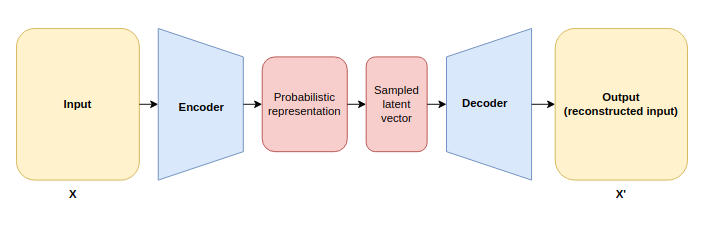
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Variational AutoEncoders (VAEs) is a type of autoencoder that extends the basic architecture to learn a probabilistic model of the data.
This allows them to generate new data similar to the original input but not identical.
The key innovation in VAEs is the introduction of a regularization term known as the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, which encourages the learned distribution to match a prior distribution, typically a standard normal distribution.
This regularization term allows VAEs to generate more diverse and realistic data than traditional autoencoders.
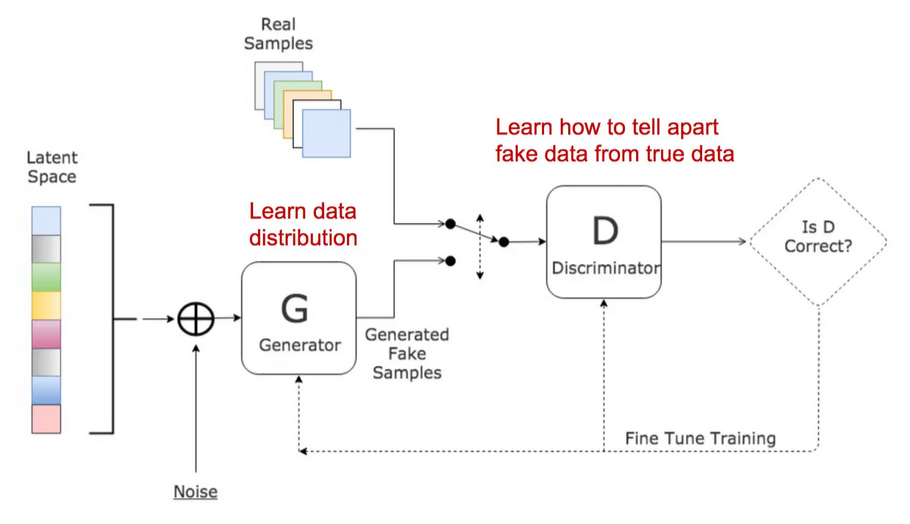
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) were introduced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014. They are a class of generative models that use two neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator, to generate new data.
The generator network takes a random noise vector as input and generates a sample from the data distribution. The discriminator network takes a sample from the data distribution and a sample from the generator network and tries to distinguish between them.
The generator network is trained to fool the discriminator network, while the discriminator network is trained to distinguish between real and fake samples.
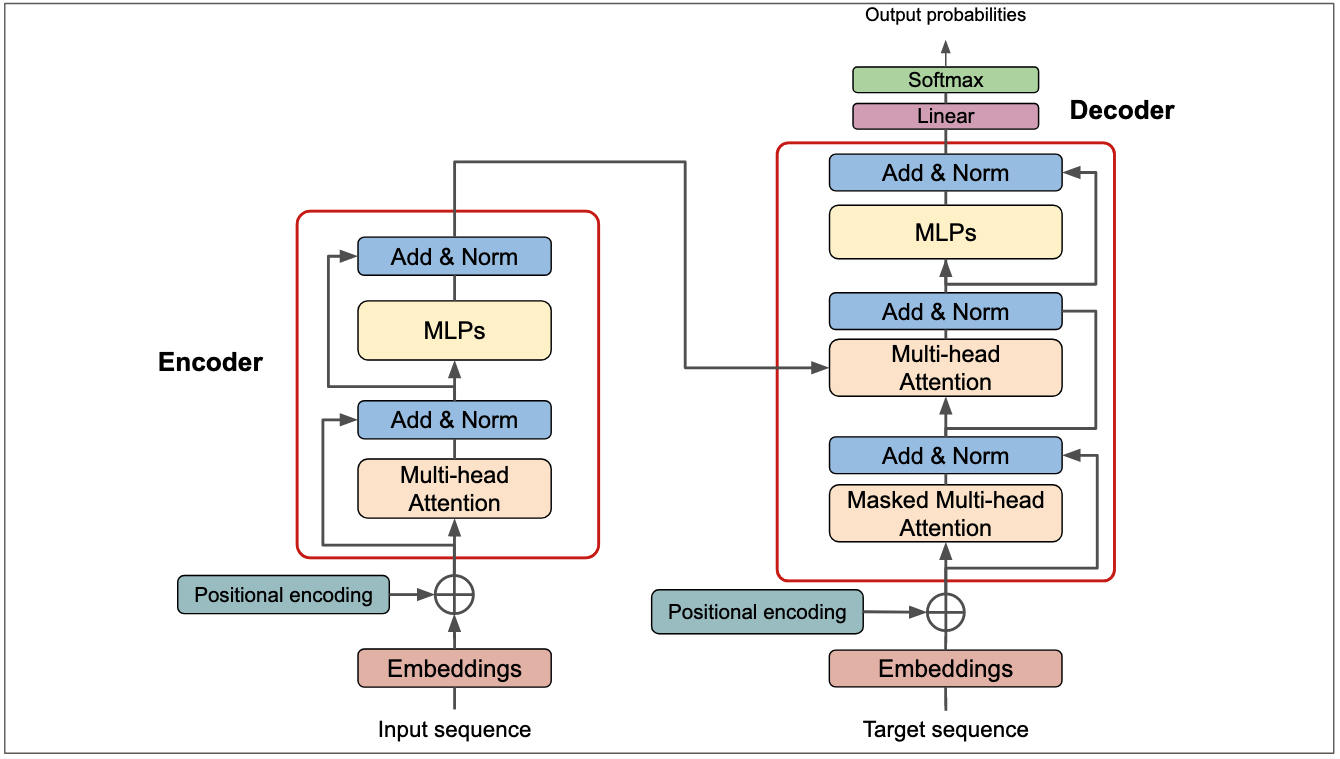
Transformers
The Transformer was introduced in 2017 by Vaswani et al.
It is a neural network architecture that uses attention mechanisms to process data sequences.
The Transformer has been used in many applications, such as machine translation, text summarization, and image captioning.
Large Language Models (LLM)
LLMs are trained on vast amounts of textual data and use transformer models to analyze and produce coherent, contextually relevant language.
They excel at tasks such as text generation, translation, and answering questions based on their training data.