ANN: Mathematical Model
Mathematical Model of an ANN
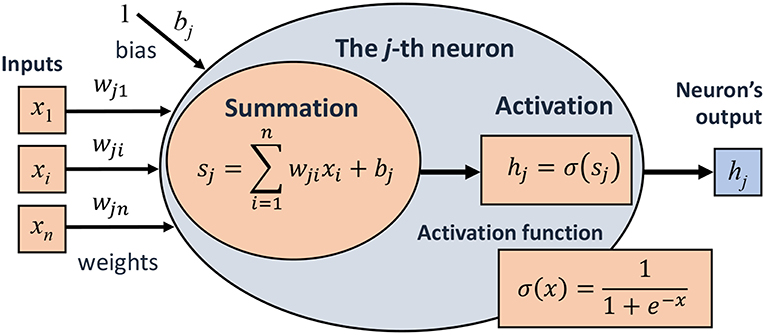
Each neuron computes a weighted sum of its inputs, adds a bias term, and applies an activation function. The output of a neuron can be represented as:
\[ y = f\left( \sum_{i=1}^{n} w_i x_i + b \right) \]
where ( w_i ) are the weights, ( x_i ) are the inputs, ( b ) is the bias, and ( f ) is the activation function.
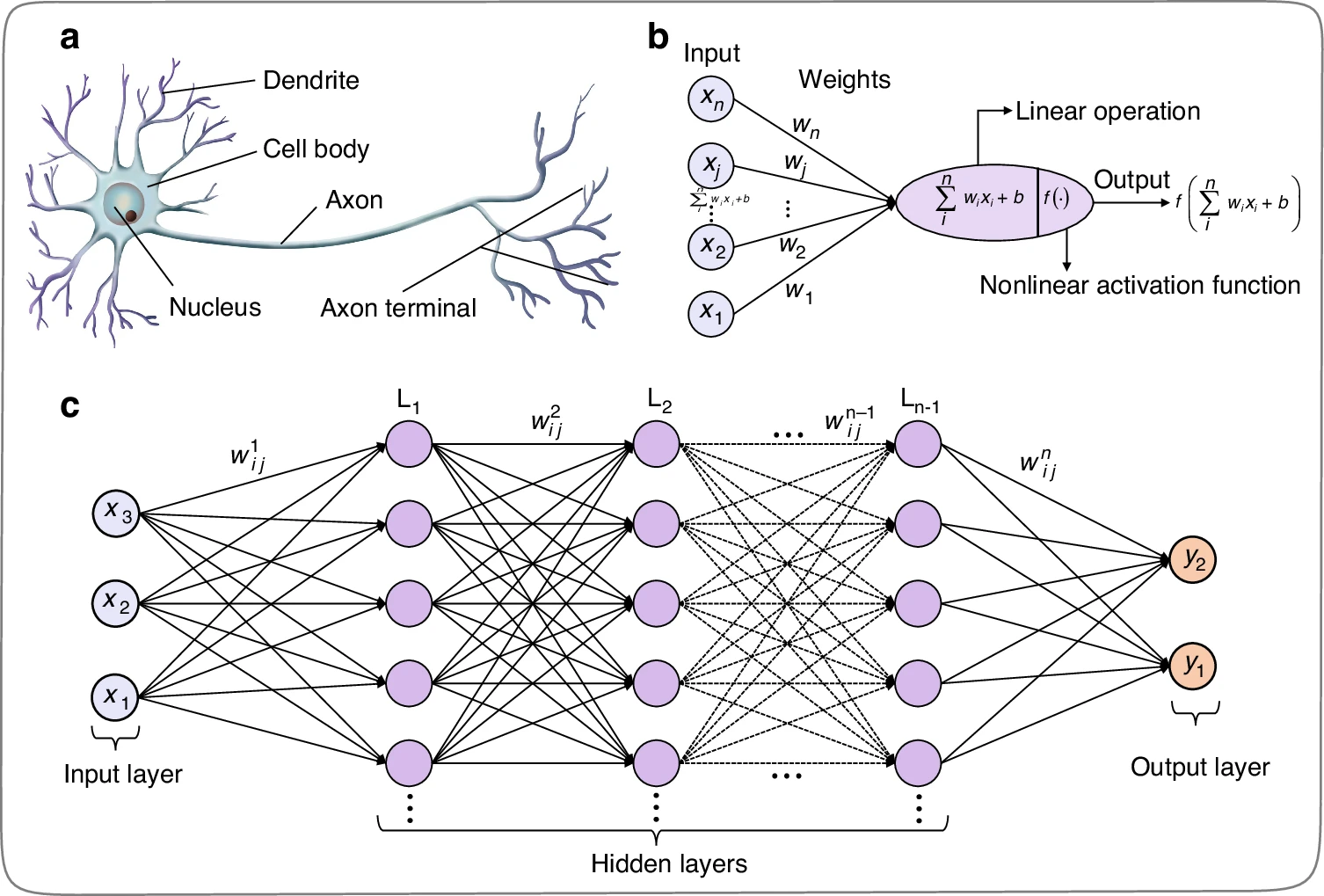
Neuron structure and artificial neural network. a Structure of biological neurons. b Mathematical inferring process of artificial neurons in multi-layer perceptron, including the input, weights, summation, activation function, and output. c Multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network
Structure of Biological Neurons
A biological neuron consists of three main components: dendrites, soma, and axon[2]. Dendrites receive input signals from other neurons. The soma, or cell body, contains the nucleus and processes information. The axon transmits signals to other neurons through synapses[2][8].
An artificial neuron in a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) mimics the biological neuron’s function:
Inputs: Represented as a vector [1] \[x = [x_1, x_2, ..., x_n]\]
Weights: Each input is associated with a weight [1] \[w_i\]
Summation: The neuron computes a weighted sum of inputs:
\[v = \sum_{i=1}^n w_i x_i + b\]
where \[b\] is the bias term[1].
Activation Function: The sum is passed through an activation function \[f\]
\[y = f(v)\]
Common activation functions include sigmoid, hyperbolic tangent, and ReLU[1][10].
Output: The result \[y\] is the neuron’s output[1].
Multi-layer Perceptron Neural Network
An MLP consists of multiple layers of interconnected neurons:
- Input Layer: Receives the initial data[3].
- Hidden Layers: Process information through weighted connections and activation functions[3].
- Output Layer: Produces the final result[3].
The network learns by adjusting weights and biases through backpropagation, minimizing a cost function[4][9]. This process allows the MLP to model complex relationships between inputs and outputs, making it suitable for various machine learning tasks[3][9].
Citations:
- Neural Networks ‐ The Mathematical Model
- The Structure of the Neuron
- Multi-Layer Perceptron Learning in TensorFlow
- YouTube Video
- Neuron - Wikipedia
- Multilayer Perceptrons in Machine Learning
- TFM Lichtner Bajjaoui Aisha
- Overview of Neuron Structure and Function
- Multilayer Perceptron Definition
- Conference Proceedings Paper