Machine Learning
Introduction
Machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on enabling computers and machines to imitate the way that humans learn, to perform tasks autonomously, and to improve their performance and accuracy through experience and exposure to more data.
UC Berkeley breaks out the learning system of a machine learning algorithm into three main parts.
A Decision Process: In general, machine learning algorithms are used to make a prediction or classification. Based on some input data, which can be labeled or unlabeled, your algorithm will produce an estimate about a pattern in the data.
An Error Function: An error function evaluates the prediction of the model. If there are known examples, an error function can make a comparison to assess the accuracy of the model.
A Model Optimization Process: If the model can fit better to the data points in the training set, then weights are adjusted to reduce the discrepancy between the known example and the model estimate. The algorithm will repeat this iterative “evaluate and optimize” process, updating weights autonomously until a threshold of accuracy has been met.
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence, which is broadly defined as the capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior. Artificial intelligence systems are used to perform complex tasks in a way that is similar to how humans solve problems.
Deep Learning and Machine Learning
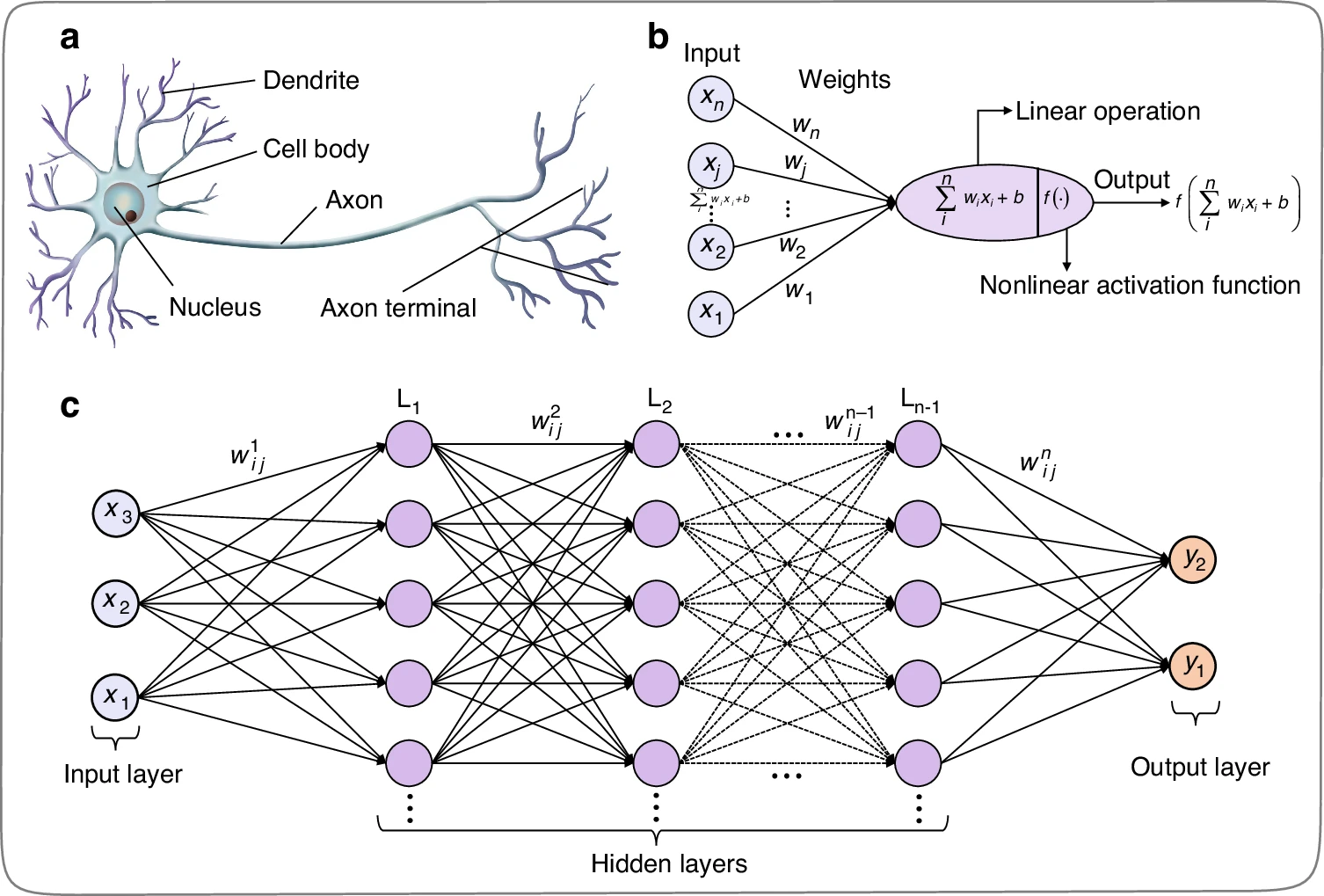
Neuron structure and artificial neural network. a Structure of biological neurons. b Mathematical inferring process of artificial neurons in multi-layer perceptron, including the input, weights, summation, activation function, and output. c Multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network
Machine Learning fields
The core idea that classifies Deep Learning as a field of Machine Learning (ML) lies in its use of artificial neural networks (ANNs) with multiple layers to automatically learn patterns and representations from data. Unlike traditional ML, which often requires manual feature engineering, deep learning models extract features hierarchically, enabling them to handle complex tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing.
Key fields in Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Semi-Supervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, Semi-Supervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning are key paradigms in machine learning. Each approach addresses different types of problems and data availability.
Supervised learning uses labeled data for training, while unsupervised learning identifies patterns in unlabeled data. Semi-supervised learning combines both, and reinforcement learning focuses on decision-making through trial and error in dynamic environments.
| Subfield | Definition | Objective | Examples | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Trains a model on a labeled dataset where each training example is paired with an output label. | Learn a mapping from inputs to outputs for predictions on unseen data. | Linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, SVMs | Classification (e.g., spam detection), regression (e.g., house prices) |
| Unsupervised Learning | Trains a model on data without labeled outputs to learn the underlying structure or distribution of the data. | Identify patterns, groupings, or relationships within the data. | Clustering (e.g., k-means, hierarchical), dimensionality reduction (e.g., PCA) | Market segmentation, anomaly detection, exploratory data analysis |
| Semi-Supervised Learning | Combines both labeled and unlabeled data for training, typically with a small amount of labeled data. | Improve learning accuracy by leveraging additional unlabeled data while benefiting from labeled examples. | Techniques using supervised methods enhanced by clustering. | Scenarios where labeling data is expensive or time-consuming (e.g., image classification) |
| Reinforcement Learning | Involves training an agent to make decisions by interacting with an environment and learning through trial and error. | Learn a policy that maximizes cumulative rewards over time. | Q-learning, deep reinforcement learning (using neural networks) | Robotics, game playing (e.g., AlphaGo), autonomous systems |
Deep Learning as distinct field
Deep learning is indeed considered a distinct field within the broader domain of machine learning.
It is characterized by its use of deep neural networks to learn complex patterns from large datasets.
Core Concept: Deep learning utilizes artificial neural networks with multiple layers (deep architectures) to automatically learn representations from data, distinguishing it from traditional machine learning methods that often rely on manual feature extraction.
Complexity Handling: Deep learning excels at managing high-dimensional data and capturing non-linear relationships, making it particularly effective for tasks like image and speech recognition.
Relationship to Other Machine Learning Subfields
Deep learning can be viewed as a specialized approach within the following main subfields of machine learning, here’s how deep learning fits into the classification of machine learning and its relationship with other fields:
- Supervised Learning:
- Definition: Involves training models on labeled datasets where the output is known.
- Deep Learning Application: Deep learning models, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), are frequently used for supervised tasks like classification and regression.
- Unsupervised Learning:
- Definition: Involves training models on unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns or structures.
- Deep Learning Application: Techniques like autoencoders and generative adversarial networks (GANs) are used in deep learning for tasks such as clustering and anomaly detection.
- Semi-Supervised Learning:
- Definition: Combines both labeled and unlabeled data for training, leveraging the strengths of both approaches.
- Deep Learning Application: Deep learning can enhance semi-supervised methods by using pre-trained models to extract features from unlabeled data.
- Reinforcement Learning:
- Definition: Involves training agents to make decisions by interacting with an environment, receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
- Deep Learning Application: Deep reinforcement learning combines neural networks with reinforcement learning principles, enabling agents to learn complex behaviors in environments with high-dimensional state spaces.
Deep learning represents a significant advancement in machine learning, offering powerful tools for both supervised and unsupervised tasks. Its ability to automatically learn features from raw data sets it apart from traditional machine learning methods, making it a critical area of research and application in modern AI systems.