Deep Learning
Overview
Deep learning is a transformative subset of machine learning that utilizes artificial neural networks (ANNs) to model complex patterns in data, inspired by the human brain’s architecture.
Characterized by its ability to process vast amounts of information through multiple interconnected layers, deep learning has driven significant advancements in various fields, including computer vision, natural language processing, and automation.[1][2]
The rise of deep learning has enabled machines to achieve performance levels that surpass human capabilities in tasks such as image recognition and language translation, marking a pivotal shift in how artificial intelligence (AI) is applied across industries.[1]
Notably, deep learning models, particularly deep neural networks (DNNs), have demonstrated remarkable success in diverse applications, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image analysis and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sequential data tasks.[3][4]
However, the technology is not without its challenges; issues related to data quality, the demand for skilled professionals, and the interpretability of complex models pose significant hurdles for practitioners and organizations aiming to leverage deep learning effectively.[5][6]
Moreover, ethical concerns regarding bias and transparency in AI decision-making processes have sparked ongoing debates about the responsible development and deployment of deep learning technologies.[7][8]
As industries increasingly rely on deep learning to enhance efficiency and innovation, understanding its foundational principles, capabilities, and limitations has become essential. The architecture of deep learning models involves intricate design choices, including layer composition and training algorithms like backpropagation, which are crucial for optimizing performance.[2][9]
With continuous research and development, the field of
deep learningis poised for further growth, presenting both opportunities and challenges that must be addressed to harness its full potential in a responsible manner.
Types of deep learning Models
Deep learning encompasses various types of models designed to address different types of data and tasks. Each model type has its unique architecture and application area, making them suitable for specific use cases.
Deep Neural Networks and Generative AI
Deep neural networks (DNNs) extend traditional neural networks by adding multiple hidden layers, which allows them to learn more complex patterns within the data. As of 2017, DNNs typically contained thousands to millions of units and connections, enabling them to perform tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing at levels that can surpass human capabilities[1]
Each layer in a DNN builds on the previous one, allowing the model to capture intricate patterns through its architecture, which can involve convolutional layers for spatial data processing, pooling layers for dimensionality reduction, and fully connected layers for final classification tasks[9][2]
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)consist of two neural networks: ageneratorand adiscriminator, which are trained simultaneously in a competitive framework.- The
generatoraims to create realistic synthetic data, while thediscriminatorevaluates the authenticity of the generated data against real data samples. - This adversarial training process helps improve the quality of generated outputs, making GANs popular in applications such as image generation, video creation, and data augmentation. Their ability to produce high-quality visuals has significantly impacted fields like art, entertainment, and gaming[11][12].
- The
- Transformer Models:
Transformermodels have gained prominence innatural language processing tasksdue to their efficiency in handling sequential data without relying on recurrence.Transformersutilize self-attention mechanisms to weigh the influence of different words in a sentence, allowing for a better understanding of context and relationships within the text.- This architecture has led to significant advancements in machine translation, text summarization, and conversational AI applications, making Transformers a crucial development in the
deep learninglandscape[3].
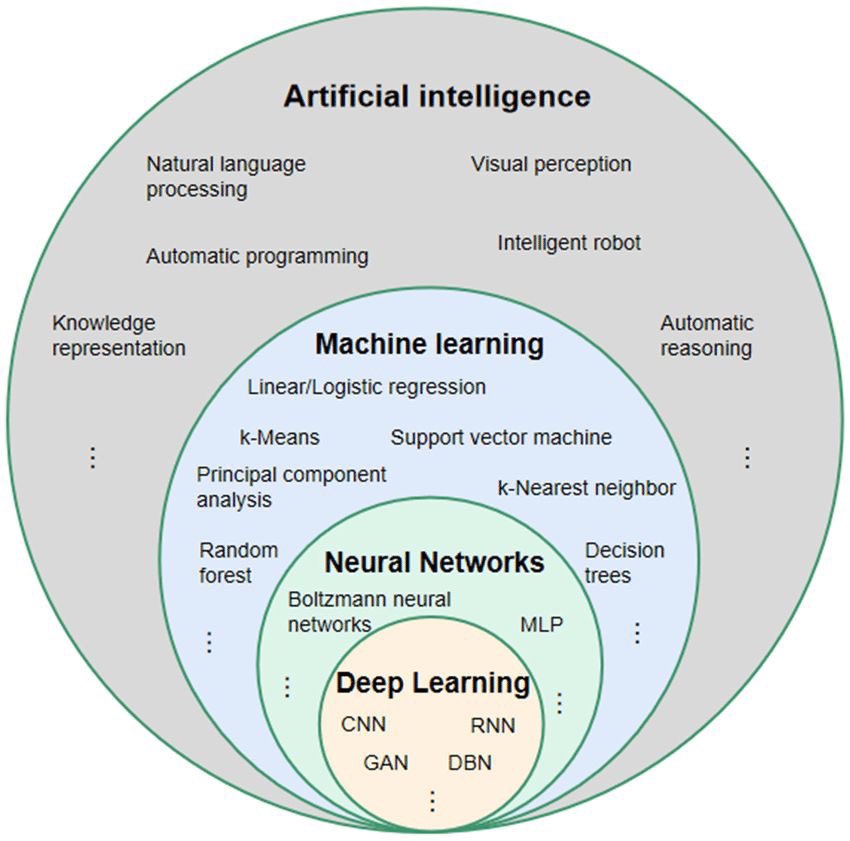
![A comparative view of AI, machine learning, deep learning, and generative AI (source [16]).](../images/deep/A-comparative-view-of-AI-machine-learning-deep-learning-and-generative-AI-source.png)